GALL BLADDER STONE
- Home
- GALL BLADDER STONE
GALL BLADDER STONES HOSPITAL - TREATMENT, REMOVAL SURGERY, DIAGNOSIS & CAUSES
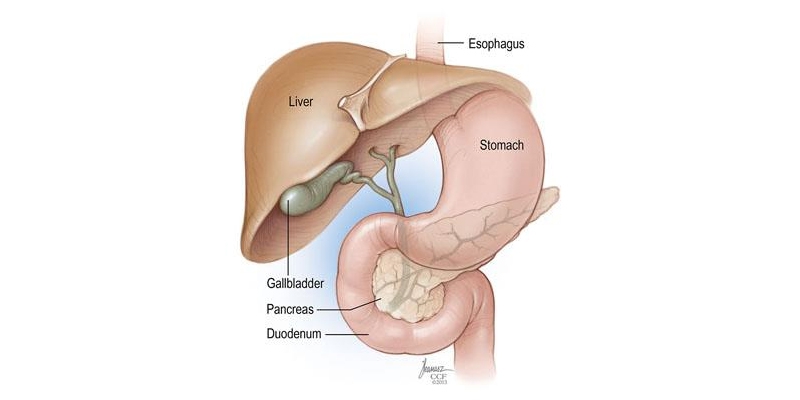
About Gallbladder Stones :
Gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ, located at the upper right part of the abdomen below the liver.
The role of the gall bladder is to store the yellow coloured liquid called bile juice that helps in proper digestion.
Whenever there is excessive cholesterol deposit, it gets hardened and forms Gallstones. These are of varying sizes ranging from the size of a grain to the size of a golf ball. Also, there may be multiple gallstones present at the same time.
Types of Gall Bladder Stones :
There are basically Two Types of Gallstones :
Gallbladder Stones Causes :
There is no clear thought on what exactly leads to the development of gallstones. However, there are a few theories, based on which doctors carry forward the treatment.
Presence of Excessive Cholesterol in Bile : Bile present in gallbladder has the ability to dissolve the cholesterol released by our liver. However, if the quantity of cholesterol released is much more than the bile can process, the excess cholesterol crystallizes and turns into hard yellow coloured stones.
Presence of too much of Bilirubin in Bile : Bilirubin is a chemical produced by the liver on break down of the red blood cells. Sometimes, the liver tends to produce excessive bilirubin due to certain medical conditions like biliary tract infections, liver cirrhosis, and few blood disorders. This excess bilirubin leads to the formation of gallstones.
Gallbladder not working Efficiently : There may be conditions when the gallbladder does not empty completely as it should. In that case, bile gets accumulated and concentrated and leads to stone formation.
Gall Bladder Stone Symptoms :
In most cases (75%), gallbladder stones show no signs or symptoms.
Often, gallstones do not show any symptoms, but when it gets stuck in the duct, it can cause blockage. In that case, you can experience one or more of the following symptoms:
Gall Bladder Stone Pain :
Gallbladder pain due to stones is sudden and intensifying. One may experience it in the middle or upper right section of the abdomen, or one may feel pain in the back at the middle of shoulder blades.
This pain may last for a few minutes or a few hours. It may get less intense or disappear to reappear. This pain is probably caused when a gallstone blocks the passage of bile that gets passed through gallbladder to the small intestine.
How Gall Bladder Stones Diagnosed?
There are several traditional and advanced procedures and tests that help doctors diagnose the condition and degree of the disease.How are Gallstones Treated?
Commonly, Gallstones require no treatment unless they cause severe symptoms like pain, and vomiting etc. Surgery is recommended in severe cases.
a.) Surgery :
b.) Nonsurgical Treatments :
Gall Bladder Stone Diet :
a) Effect of Food on Gallbladder : Being a small, delicate yet important organ, it is important to consume a healthy diet full of nutrients to maintain its health. While some foods help in improving its function, others can initiate and aggravate the gallbladder problems.
b) Foods - Good for Gallbladder : The key to having a healthy gallbladder is to have a well-balanced diet having fruits, and vegetables, which have loads of nutrients, high in calcium, vitamins C, and B and fiber. Also, eating plant-based protein like beans, nuts, lentils, tofu, and tempeh are very good for gallbladder.
It is best to Incorporate Following Foods in Your Diet for a Healthy Gallbladder :
Foods Not Good for Your Gallbladder :
It is best to avoid the foods which are high in fat and processed foods. Vegetable oils are difficult to break down and cause gallbladder problems.
Gall Bladder Stone Risk Factors :
There is not much information about the exact causes of formation of gallstones. Still, there are some observances about risk factors of formation of gallstones.
Women are observed to have more tendencies to develop this problem. Moreover, pregnant women, women on hormone replacement therapy, and those using hormone birth control are at increased risk of having gallstones.
Besides, there are other risk factors which are common to both genders. These are as follows :
When to see a doctor?
When a gallstone blocks the duct from where gallbladder releases the bile, it can lead to serious problems like inflammation and infection. It is called acute cholecystitis and is a medical emergency.